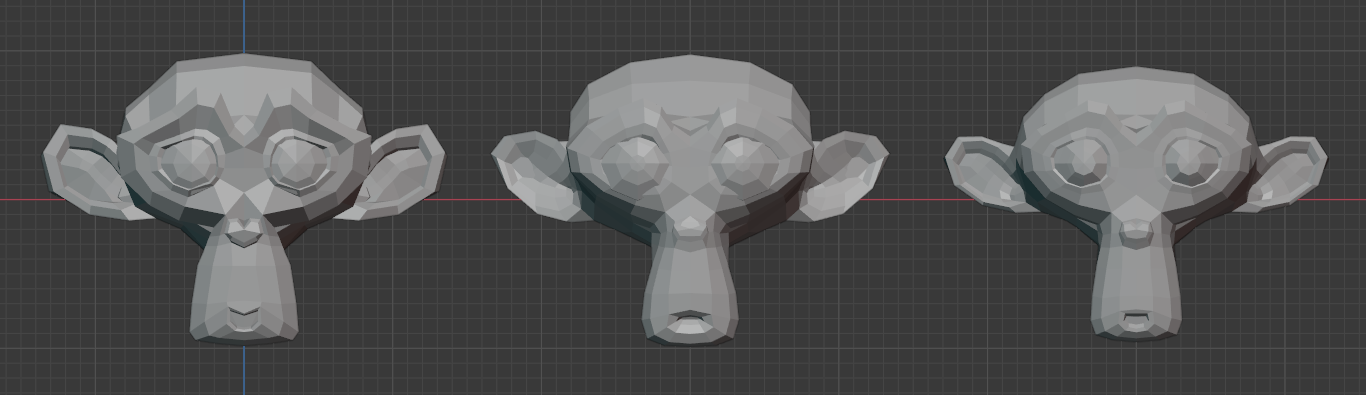
Smooth¶
This effect will move vertices to make the mesh more smooth.
- Input
polygonal mesh
- Output
polygonal mesh
- VTK classes
vtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter,vtkSmoothPolyDataFilter- Preserves topology
Yes
- Multithreaded
Yes (Windowed sinc mode)
Options¶
- Mode
Windowed sinc mode (1) – creates a more nuanced effect, tends to preserve features better. It does not shrink the mesh.
Laplacian mode (2) – creates a mode uniform smoothing effect, tends to eliminate more features. Stronger smoothing also shrinks the mesh as a side effect. This is akin to Blender Laplacian Smooth Modifier.
- Iterations
Number of smoothing rounds. Higher number means stronger effect and longer computation time.
- Factor
This parameter also affects smoothing strength, with higher values creating stronger effect. Precise meaning depends on the mode.
In Windowed sinc mode, this is the passband of the windowed sinc filter (possible values: from 0.0 to 2.0).
In Laplacian mode, this is the relaxation factor. Setting this to a higher value has similar effect as increasing the number of iterations, with the same computation time, but it may affect quality.
- Boundary smoothing
Whether to move vertices of boundary edges.
- Feature edge smoothing
Whether to analyze edges to better preserve input shape.
- Feature angle
If Feature edge smoothing is enabled, this determines minimum angle between faces to be considered a “major” edge.
- Edge angle
If Feature edge smoothing is enabled, this determines minimum angle between faces to be considered a “minor” edge.
Note
For a more in-depth explanation of the modes and options, see VTK documentation:
Windowed sinc mode: vtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter
Laplacian mode: vtkSmoothPolyDataFilter